Safe Steps: Mastering Outdoor Handrail Codes

Navigating the world of building codes can feel like traversing a complex maze, especially when it comes to seemingly minor details like handrails. But these "minor" details are critical for safety, and outdoor stair handrail regulations are no exception. Understanding and adhering to these codes is paramount for creating a safe and accessible environment for everyone.
Outdoor steps, while providing access and enhancing curb appeal, can pose significant safety risks without proper handrails. Regulations surrounding outdoor step handrails exist to mitigate these risks. These codes outline specific requirements for handrail height, materials, extensions, and other crucial aspects, ensuring consistent safety standards across various properties and public spaces. Ignoring these guidelines can not only lead to accidents but also potential legal liabilities.
The history of handrail codes is rooted in the recognition of the inherent dangers associated with stairs and elevated surfaces. As architectural design evolved and building practices became more standardized, the need for uniform safety measures became apparent. Over time, these practices were codified to protect the public and ensure a baseline level of safety in both residential and commercial settings. Early codes focused primarily on basic dimensions and structural integrity. Modern codes have evolved to encompass accessibility concerns, incorporating guidelines that address the needs of individuals with disabilities and promoting universal design principles.
Why are these codes so important? The primary reason, of course, is safety. Handrails provide crucial support and stability, preventing falls and injuries. They are especially critical for children, the elderly, and people with mobility challenges. Adhering to outdoor handrail codes demonstrates a commitment to public safety and minimizes the risk of accidents. Moreover, compliance with these regulations prevents legal complications and ensures properties meet building inspection requirements.
Understanding the specifics of your local outdoor step handrail code is crucial. While general guidelines exist, variations can occur based on regional and local jurisdictions. Consulting your local building authority or a qualified professional is the best way to ascertain the precise regulations applicable to your project. This proactive approach will ensure your handrail installation meets all necessary requirements.
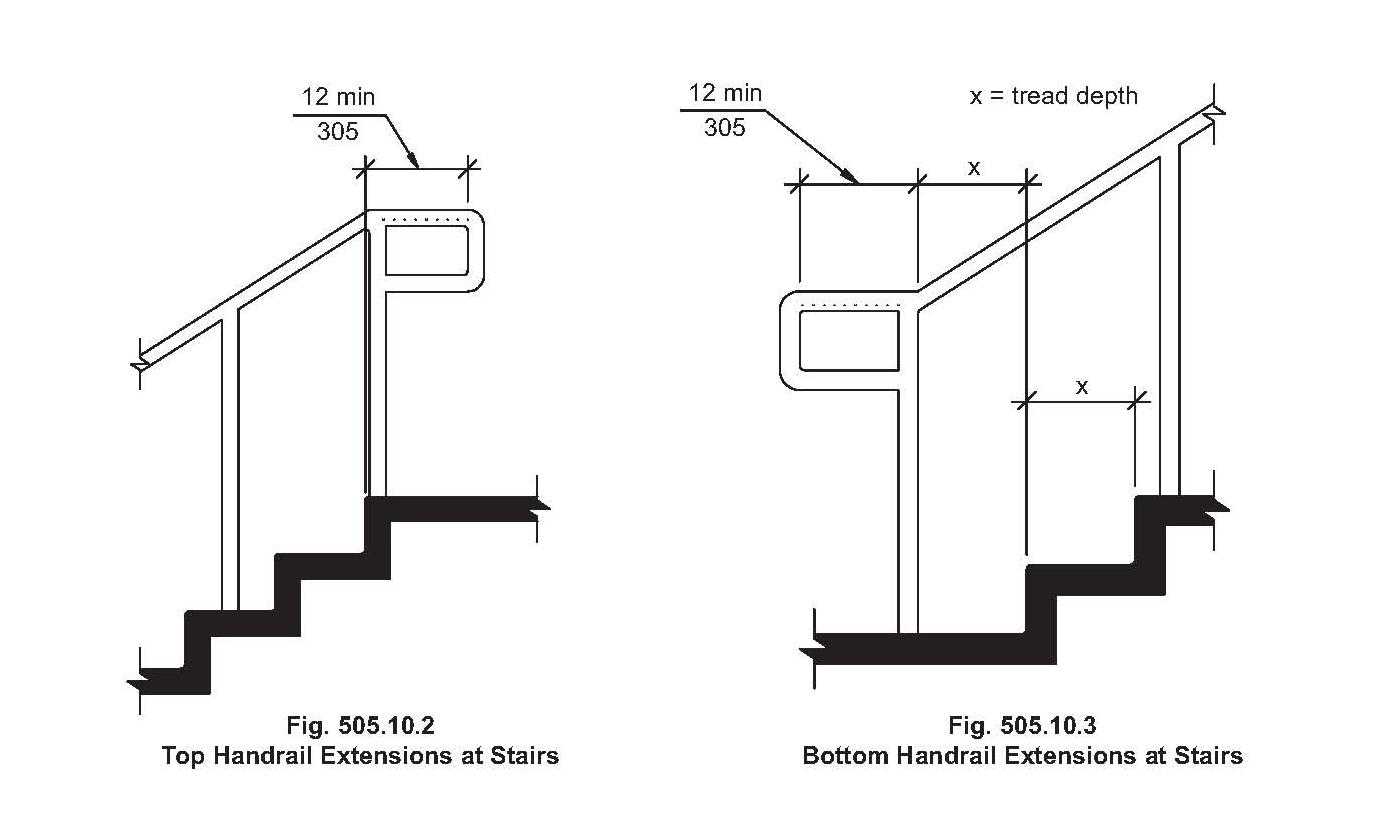
A handrail, in its simplest definition, is a rail designed to be grasped by the hand for support. In the context of outdoor steps, handrails are typically attached to posts or wall brackets and extend along the length of the staircase. Codes typically specify minimum and maximum handrail heights, distances from the wall, and requirements for continuous grasping surfaces. For example, a common code requirement is a handrail height between 34 and 38 inches, measured vertically from the nosing of the stair treads.
One of the benefits of adhering to outdoor handrail codes is enhanced safety. Properly installed handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls, particularly on wet or icy steps. Another benefit is improved accessibility. Handrails make it easier for individuals with mobility limitations to navigate stairs, promoting inclusivity and independent living. Finally, compliance with codes ensures peace of mind, knowing that your property meets established safety standards.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Following Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Initial Cost |
| Improved Accessibility | Potential Design Limitations |
| Code Compliance | Maintenance Requirements |
Best Practices:
1. Consult local codes: Always check with your local building authority.
2. Use appropriate materials: Choose durable, weather-resistant materials.
3. Secure installation: Ensure handrails are firmly attached.
4. Proper height: Adhere to specified height requirements.
5. Continuous grasping surface: Avoid interruptions in the handrail.
FAQ:
1. What is the standard handrail height? Answer varies by location.
2. Do I need a handrail on both sides of the stairs? Often yes, but check local codes.
3. What materials are acceptable for outdoor handrails? Typically metal, wood, or composite.
4. Can I install the handrail myself? Yes, but professional installation is recommended.
5. What are the penalties for not complying with handrail codes? Varies by jurisdiction, may include fines.
6. How often should handrails be inspected? Regularly, especially after severe weather.
7. Where can I find my local handrail codes? Contact your local building authority.
8. Are there exceptions to handrail codes? Possibly, check local regulations.
In conclusion, adhering to outdoor handrail codes is not just about checking a box on a building permit; it's about creating a safe and accessible environment for everyone. From enhancing safety and promoting accessibility to ensuring legal compliance and peace of mind, the benefits are undeniable. By understanding the regulations, engaging in proper planning, and prioritizing professional installation, you can transform your outdoor steps from potential hazards into secure and welcoming access points. Take the time to research your local codes and invest in properly installed handrails – it's an investment in the well-being of everyone who uses your steps. Remember, a little foresight and adherence to these guidelines can prevent accidents and create a more inclusive environment. Don't wait for an incident to occur; take action now to ensure your steps are safe and code-compliant.
Mastering the art of introductions in academic papers
Understanding the impact of images of single fathers
Conquering the open road mastering the silverado 2500s dimensions