Understanding GS Pay Scale Adjustments and Growth

Navigating the complexities of federal employment requires a solid understanding of the General Schedule (GS) pay system. A critical aspect of this system is the structured approach to pay increases, which allows employees to anticipate and plan for their financial future. This article delves into the mechanisms of GS pay progression, providing a comprehensive overview of how these advancements impact federal employees.
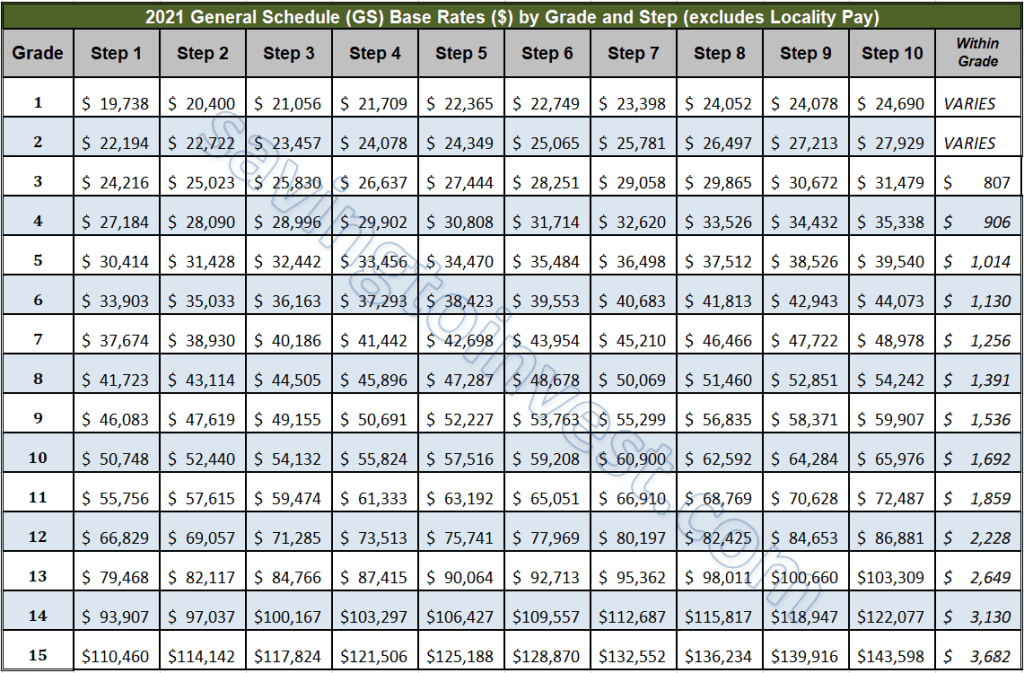
The GS pay scale, a cornerstone of federal compensation, is a standardized system that ensures fair and equitable pay for government employees. This structured framework establishes distinct pay grades and steps, providing a clear path for salary growth based on performance and tenure. Understanding how these salary adjustments work is essential for any federal employee seeking to maximize their earning potential.
Progression within the GS pay scale involves two primary mechanisms: annual salary increases and within-grade step increases. Annual increases are generally tied to adjustments for cost of living and are applied across the board to all GS employees. Within-grade step increases, on the other hand, are based on satisfactory performance and length of service within a specific grade. These incremental increases provide a predictable pathway for salary growth within a given pay grade.
The history of the GS pay scale dates back to the Classification Act of 1923, which aimed to standardize federal positions and compensation. Since its inception, the system has undergone numerous revisions to address changing economic conditions and ensure equitable pay. The importance of these periodic adjustments lies in maintaining the competitiveness of federal salaries and attracting and retaining qualified individuals in government service.
One of the main issues surrounding GS pay scale increases is the debate over their adequacy in keeping pace with inflation and private sector salaries. Ensuring that federal compensation remains competitive is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent in the government workforce. Therefore, understanding the factors that influence these increases, such as locality pay adjustments and special rate supplements, is paramount for both employees and policymakers.
Within-grade increases (WGIs) are periodic step increases within a single GS grade. Employees typically receive a WGI after completing a prescribed period of acceptable performance. For example, an employee at GS-9, Step 1, might advance to GS-9, Step 2, after one year of service, then to Step 3 after another year, and so on.
Benefits of GS pay scale increments include predictable income growth, motivation for performance improvement, and enhanced employee retention. Predictable income growth allows for financial planning. Motivation for performance improvement stems from the direct link between performance and salary increases. Enhanced employee retention is a result of the clear career progression path.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GS Pay Scale Increments
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable salary growth | Limited earning potential compared to the private sector |
| Fair and transparent system | Potential for pay compression at higher grades |
| Motivates performance | Slow progression at higher steps |
Best Practice: Understand your specific GS pay scale and the requirements for step increases.
FAQ: How are locality pay adjustments calculated?
Answer: Locality pay is based on geographic location and is designed to reflect the cost of living in a particular area.
Tips and tricks: Regularly review your agency's pay policies and stay informed about any changes to the GS pay scale.
In conclusion, navigating the GS pay scale and its increment system is vital for any federal employee. Understanding how these adjustments work empowers employees to plan their careers effectively and maximize their earning potential. While challenges exist, such as maintaining pay competitiveness with the private sector, the structured and transparent nature of the GS system provides a framework for fair and equitable compensation. By staying informed about pay policies and actively engaging in performance improvement, federal employees can fully leverage the benefits of the GS pay scale and ensure their financial well-being. Taking the time to understand these mechanisms is not only beneficial for individual employees but also contributes to a more effective and efficient federal workforce overall. Resources for further exploration include the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) website and publications on federal compensation.
The sss rankers epic comeback
Bmw x7 manhattan green a luxurious suv in a unique hue
Unlocking canine communication with the in the doghouse podcast