Understanding the GS Pay Scale System

Are you considering a career with the federal government? Understanding the General Schedule (GS) pay system is crucial for anyone exploring federal employment opportunities. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the GS pay scale, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate this complex system.
The GS pay scale serves as the foundation for determining the salaries of the vast majority of federal government employees. This standardized system ensures fair and consistent compensation based on factors like job responsibilities, experience, and geographic location. From entry-level positions to senior executive roles, the GS pay scale provides a structured framework for career progression and financial stability within the federal workforce.
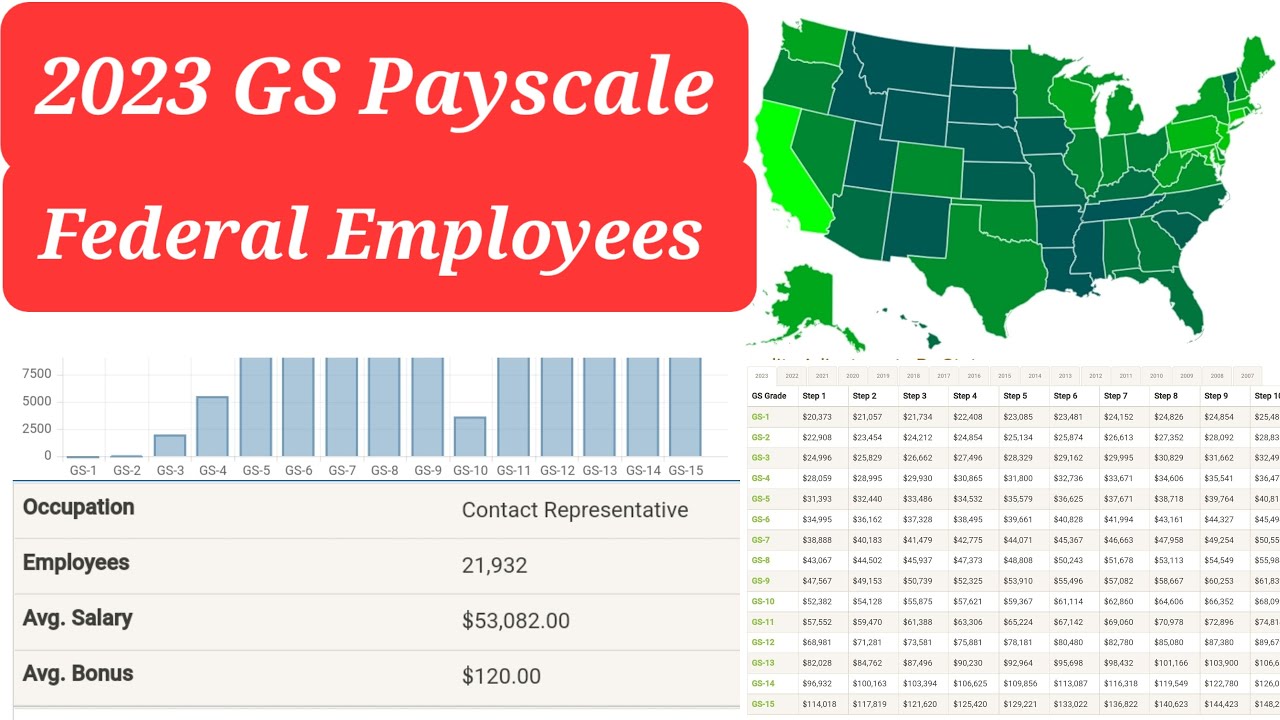
The GS pay scale is divided into 15 grades, ranging from GS-1 to GS-15. Each grade is further subdivided into 10 steps, representing incremental increases in salary within that grade. Progression through the steps is typically based on time in service and satisfactory performance. This structured approach allows employees to anticipate salary increases and plan for their financial future.
Beyond the base GS pay grade and step, locality pay adjustments are incorporated to reflect the cost of living in different geographic areas. This ensures that federal employees' salaries remain competitive with the private sector in their respective locations. Understanding how locality pay affects your potential earnings is essential when considering federal job opportunities in various parts of the country.
Navigating the complexities of the GS pay scale can seem daunting at first, but with the right resources and information, you can gain a clear understanding of how this system works. This article will equip you with the knowledge you need to interpret salary information, understand pay progression, and make informed decisions about your federal career path.
The GS pay system has a rich history, originating in the Classification Act of 1923. This act aimed to standardize federal positions and create a fair and equitable pay structure. Over the years, the system has evolved to accommodate changing economic conditions and workforce needs. Its importance lies in its ability to provide a consistent and transparent compensation framework for federal employees.
A key aspect of the GS pay scale is the concept of "within-grade increases," often referred to as step increases. These increases occur at regular intervals, typically every one, two, or three years, depending on the employee's step level. They provide a predictable path for salary growth within a specific GS grade.
Benefits of the GS pay system include: predictable salary increases, locality pay adjustments, and job security. These benefits offer stability and a clear career trajectory within the federal government.
To determine your potential salary under the GS pay scale, you'll need to identify the appropriate GS grade for the position you're interested in, along with the applicable locality pay area. Online resources, such as the official OPM website, provide detailed pay tables that outline salary information for each GS grade and step in various locations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Structured and Transparent | Limited Negotiation Power |
| Regular Step Increases | Potential Salary Compression |
| Locality Pay Adjustments | Bureaucracy and Regulations |
Best practices for understanding the GS pay scale include researching your desired position, using online resources like the OPM website, and consulting with current federal employees.
Real-world examples of GS pay scale usage can be found in job postings for federal agencies. These postings typically specify the GS grade and salary range for the advertised positions.
Challenges related to the GS pay scale might include understanding the complexities of locality pay or navigating the promotion process. Solutions often involve seeking clarification from human resources personnel or consulting with experienced colleagues.
Frequently asked questions about the GS pay scale include: "How are locality pay adjustments calculated?" and "How do I advance to a higher GS grade?"
Tips and tricks for maximizing your earnings under the GS pay scale include pursuing advanced degrees or certifications, seeking opportunities for promotion, and understanding the specific requirements for within-grade increases.
In conclusion, the General Schedule (GS) pay scale plays a vital role in the compensation of federal government employees. Its structured approach, combined with locality pay adjustments and regular step increases, provides a framework for predictable career progression and financial stability. By understanding the intricacies of this system, prospective and current federal employees can make informed decisions about their career paths and maximize their earning potential. Utilizing online resources, consulting with experienced colleagues, and staying informed about changes to the GS pay scale are crucial steps in navigating this complex system and ensuring a rewarding federal career. Take the time to thoroughly research the GS system, explore different career paths, and understand how this system impacts your long-term financial goals. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions and build a successful career within the federal government.
Unlocking the power of free birthday images
Lexus is350 lug nut size everything you need to know
Toyota camry check engine light blinking dont panic yet